Introduction
In virtual infrastructures, especially in large data centers, ensuring high availability and eliminating single points of failure is crucial. Microsoft addresses this need with Failover Clustering technology, which can be implemented in a Hyper-V environment. This allows multiple Hyper-V hosts or nodes to take over the workload if one host fails, ensuring service continuity.
Although Hyper-V primarily manages resources at the physical machine level, Microsoft Failover Clustering provides protection for virtual machines by minimizing downtime during failures. Failover Clustering operates alongside Hyper-V, offering enhanced resilience. It uses its dedicated Failover Cluster Manager for administration, allowing streamlined management of clustered nodes and ensuring virtual machine availability in the event of host failure.
Key Use cases
Discovery Use cases
- It discovers the Windows Hyper-V Cluster components.
- Publishes relationships between resources to have a topological view and ease of maintenance.
Monitoring Use cases
- Provides metrics related to job scheduling time and status etc.
- Concern alerts will be generated for each metric to notify the administrator regarding the issue with the resource.
Supported Target Versions
| Validated the application by executing powershell script against "Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Datacenter 10.0.17763 Build 17763.3770" |
Prerequisites
OpsRamp Classic Gateway(Linux) 14.0.0 and above.
OpsRamp NextGen Gateway 14.0.0 and above.
Note: OpsRamp recommends using the latest Gateway version for full coverage of recent bug fixes, enhancements, etc.Powershell cmdlets have the following prerequisites:
- Windows domain User should be able to do powershell remoting
Enable-PSRemoting -Force - Windows domain user should be added to “Remote Management users” group
net localgroup “Remote Management Users” /add < user > - Windows domain user should be added to “Performance monitor users” group
net localgroup “Performance monitor users” /add < user > - Add OpsrampGatewayIp to the TrustedHosts list on the target machine to allow the powershell connection from gateway to the target machine.
- To add TrustedHosts use the following command:
- To allow any host:
Set-Item WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts -Force -Value * - To allow a specific host: Set-Item WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts -Force -Concatenate -Value <OpsRampGatewayIp>
- Setup and restart the WinRM service for the changes to reflect
- To set up: Set-Service WinRM -StartMode Automatic
- Restart using: Restart-Service -Force WinRM
- Windows domain User should be able to do powershell remoting
Granting Remote DCOM Rights
- To grant users DCOM rights, log on to each monitored system and complete the following procedure:
- Go to command prompt and enter dcomcnfg
- Navigate to component services > computers > My computer and then right click and select Properties. Then go to the COM Security tab.
- Under Access Permissions, go to edit limits and add the domain non-admin user and enable both local and remote access then click OK.
- In Launch and Activation permissions, go to edit limits, add the domain non-admin user and check all boxes, and click OK.
- To grant users DCOM rights, log on to each monitored system and complete the following procedure:
Granting Remote WMI Rights
- To give the user remote WMI rights, log on to each system to be monitored and complete the following procedure:
- Go to computer management, under Services and Applications select WMI Control.
- Right-click WMI control and go to Properties. Select the Security tab.
- Select root and click Security.
- Add the domain non-admin user, and check the boxes for execute methods, enable account, remote enable, and reas security.
- Click Advanced, select added non-admin domain user and click Edit. Then for Applies, select namespace and sub namespaces in the dropdown.
- Click OK three times .
- To give the user remote WMI rights, log on to each system to be monitored and complete the following procedure:
For monitoring services like windows cluster service, windows domain users to be a part of Local Administrators group we are using win32_Service class for fetching the details.
- refer to below link:
Get-WmiObject - If you do not want to add the user to local administrator group, you can use Security descriptors for monitoring the services.
- For that we have to do the configuration as below:
Refer to Windows failover cluster monitoring.
- refer to below link:
Windows domain user should be granted read-only access to cluster
Grant-ClusterAccess -User <domain\user> -ReadonlyOpen ports and add user in all nodes and cluster
- Opsramp gateway should be able to access cluster and nodes.
- Ports to be opened are 5985 and 5986.
Note: By default, WS-Man and PowerShell remoting use port 5985 and 5986 for connections over HTTP and HTTPS, users should be present in nodes and cluster.
The following prerequisites enable monitoring of Hyper-V guest VM and virtual switch resources with a non-administrator user account.
Option 1: Using Computer Management (GUI)
- Click Start → Run, type
lusrmgr.msc, and click OK. - In Local Users and Groups, select Groups, then choose Hyper-V Administrators.
- Right-click Hyper-V Administrators and select Properties.
- Click Add, enter the local user account name, click Check Names, and then click OK.
- Click Apply, then OK. Close the Properties window, and restart Windows to apply the changes.
- Click Start → Run, type
Option 2: Using PowerShell (Recommended)
Run PowerShell as Administrator:
To add domain user:
Add-LocalGroupMember -Group "Hyper-V Administrators" -Member "DOMAIN\username"To add local user:
Add-LocalGroupMember -Group "Hyper-V Administrators" -Member "username"Command to verify:
Get-LocalGroupMember "Hyper-V Administrators"
Note:If the non-administrator user account is not added to the Hyper-V Administrators group, Hyper-V virtual machine, and virtual switch discovery and monitoring will not function in OpsRamp.
Hierarchy of Windows Hyper-V Cluster
- For Windows Hyper-V Cluster, Hierarchy is as follows
- Windows HyperV Cluster
- Windows HyperV Server
- Windows HyperV Virtual Switch
- Windows HyperV Host Disk
- Windows HyperV Guest VM
- Windows HyperV Cluster Role
- Windows HyperV Cluster Shared Volume
- Windows HyperV Cluster Disk
- Windows HyperV Server
- Windows HyperV Server
- Windows HyperV Virtual Switch
- Windows HyperV Host Disk
- Windows HyperV Guest VM
Supported Metrics
Click here to view the supported metrics
| Native Type | Metric Name | Display Name | Metric Label | Units | Application Version | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows HyperV Cluster | windows_hyperv_cluster_network_State | windows HyperV Cluster Network State | Availability | - | 1.0.0 | HyperV cluster network state.Possible states are:Unavailable: 0, Down: 1, Partitioned: 2, Unknown: 3, Up: 4 |
| windows_hyperv_cluster_OnlineNodesCount | Windows HyperV Cluster Online Nodes Count | Availability | count | 1.0.0 | HyperV cluster online nodes count | |
| windows_hyperv_cluster_NodeHealth | Windows HyperV Cluster Node Health | Availability | % | 1.0.0 | HyperV cluster node health. | |
| Windows HyperV Server | windows_hyperv_server_IdleCPUUtilization | Windows HyperV Server Idle CPU Utilization | Usage | % | 1.0.0 | HyperV server idle cpu utilization |
| windows_hyperv_server_NetworkAdaptersBytesTotalPerSec | Windows HyperV Server Network Adapter Total BytesPerSec | Performance | Bps | 4.0.0 | This metric measures how many bytes of data are transferred or processed per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_LegacyNetworkAdaptersBytesReceivedPerSec | Windows HyperV Server Legacy Network Adapter Received BytesPerSec | Performance | Bps | 4.0.0 | This metric measures the number of bytes received per second by a network adapter, particularly in older or legacy network hardware. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_LegacyNetworkAdaptersBytesSentPerSec | Windows HyperV Server Legacy Network Adapter Bytes Sent PerSec | Performance | Bps | 4.0.0 | This metric provides insight into how much data is being sent out by the network adapter over a period of one second. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_LegacyNetworkAdaptersBytesDropped | Windows HyperV Server Legacy Network Adapter Bytes Dropped | Performance | Bps | 4.0.0 | The total amount of data (in bytes) that was sent to a network adapter but could not be processed or successfully transmitted due to various reasons, and therefore was "dropped". | |
| windows_hyperv_server_LegacyNetworkAdaptersFramesSentPerSec | Windows HyperV Server Legacy Network Adapter Frames Sent PerSec | Performance | packets/sec | 4.0.0 | This metric refers to the rate at which network frames (packets) are transmitted by a legacy network adapter, measured in frames per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_SwapMemoryUsageInGB | Windows HyperV Server Swap Memory Usage in GB | Usage | GB/sec | 4.0.0 | This metric measures the virtual memory that the operating system uses to extend physical RAM (Random Access Memory) when it is fully utilized. | |
| windows_hyperv_disk_LogicalDiskTransferPerSec | Windows HyperV Server Logical Disk Bytes Per Sec | Performance | Bps | 4.0.0 | This metric measures the rate at which thedata byte is being transferred to or from a logical disk. | |
| windows_hyperv_disk_LogicalDiskQueueLength | Windows HyperV Server Logical Disk Queue Length | Performance | 4.0.0 | This metric provides insight into how many read and write requests are queued up at any given time, waiting to be serviced by the disk. | ||
| windows_hyperv_disk_Utilization | Windows HyperV Server Disk Utilization | Usage | % | 4.0.0 | This metric provides insight into how much of the disk's capacity is being used for I/O operations. | |
| windows_hyperv_disk_LogicalDiskBytesPerSec | Windows HyperV Server Logical DiskTransfer Per Sec | Performance | IOPS | 4.0.0 | This metric measures the rate at which data is being transferred to or from a logical disk. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_PhysicalMemoryUtilization | Windows HyperV Server Physical Memory Utilization | Usage | % | 5.0.0 | HyperV server physical memory utilization | |
| windows_hyperv_server_GuestCPUUtilization | Windows HyperV Server Guest CPU Utilization | Usage | % | 1.0.0 | The percentage of time spent by the virtual processor in guest code. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_HypervisorCPUUtilization | Windows HyperV Server Hypervisor CPU Utilization | Usage | % | 1.0.0 | The percentage of time spent by the virtual processor in hypervisor code. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_TotalCPUUtilization | Windows HyperV Total CPU Utilization | Usage | % | 1.0.0 | The percentage of time spent by the virtual processor in guest and hypervisor code. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_system_services_HealthState | Windows HyperV System Services Health State | Availability | 1.0.0 | HyperV system services health state.Possible values are - 0 : Unknown , 5 : OK , 10 : Degraded/Warning , 15 : Minor failure , 20 : Major failure , 25 : Critical failure , 30 : Non-recoverable error , 35 : DMTF Reserved | ||
| windows_hyperv_server_AvailableMBytes | Windows HyperV Server Available MBytes | Performance | MB | 1.0.0 | HyperV server available Mbytes. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_PageFileUsage | Windows HyperV Server Page File Usage | Usage | GB | 1.0.0 | HyperV server page file usage. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_VirtualTLBPages | Windows HyperV Server Virtual TLB Pages | Performance | count | 1.0.0 | HyperV server virtual TLB pages. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_DepositedPages | Windows HyperV Server Deposited Pages | Performance | count | 1.0.0 | HyperV server deposited pages. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_TotalPhysicalMemory | Windows HyperV Server Total Physical Memory | Performance | GB | 1.0.0 | HyperV server total physical memory. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_Virtual_Memory | Windows HyperV Server Virtual Memory | Performance | GB | 1.0.0 | HyperV server virtual memory | |
| windows_hyperv_server_TotalRemotePhysicalPages | Windows HyperV Server Total Remote Physical Pages | Performance | count | 1.0.0 | HyperV server total remote physical pages. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_NetworkAdaptersBytesReceived | Windows HyperV Server Network Adapter BytesReceivedPerSec | Performance | Bps | 1.0.0 | HyperV network adapter bytes received per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_NetworkAdaptersPacketsSent | Windows HyperV Server Network Adapter Packets Sent | Performance | Bps | 1.0.0 | HyperV network adapter bytes received per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_NetworkAdaptersBytesSent | Windows HyperV Server Network Adapter Bytes Sent | Performance | Bps | 1.0.0 | HyperV network adapter bytes sent. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_NetworkAdaptersPacketsReceived | Windows HyperV Server Network Adapter Packets Received | Performance | packets/sec | 1.0.0 | HyperV network adapter packets received. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_NetworkAdaptersPackets | Windows HyperV Server Network Adapter Packets | Performance | packets/sec | 1.0.0 | HyperV network adapter packets per second. | |
| Windows HyperV Virtual Switch | ||||||
| windows_hyperv_server_VirtualSwitchStatus | Windows HyperV Server Virtual Switch Status | Availability | 8.0.0 | HyperV virtual switch status. Possible values are OK: 0, ERROR: 1, DEGRADED: 2, UNKNOWN: 3, PRED FAIL: 4, STARTING: 5, STOPPING: 6, SERVICE: 7, STRESSED: 8, NONRECOVER: 9, NO CONTACT: 10, LOST COMM: 11 | ||
| windows_hyperv_server_VirtualSwitchHealthState | Windows HyperV Server Virtual Switch Health State | Availability | 8.0.0 | HyperV virtual switch health state. Possible values are OK : 5, MAJOR FAILURE : 20, CRITICAL FAILURE : 25 , OTHER : 1 | ||
| windows_hyperv_server_VirtualSwitchPacketsReceived | Windows HyperV Server Virtual Switch Packets Received | Performance | packets/sec | 1.0.0 | HyperV virtual switch packets received per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_VirtualSwitchBytesReceived | Windows HyperV Server Virtual Switch Bytes Received | Performance | Bps | 1.0.0 | HyperV virtual switch bytes received per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_VirtualSwitchPackets | Windows HyperV Server Virtual Switch Packets | Performance | packets/sec | 1.0.0 | HyperV virtual switch packets per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_VirtualSwitchBytesSent | Windows HyperV Server Virtual Switch Bytes Sent | Performance | Bps | 1.0.0 | HyperV virtual switch bytes sent per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_VirtualSwitchBytes | Windows HyperV Server Virtual Switch Bytes | Performance | Bps | 1.0.0 | HyperV virtual switch bytes per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_server_VirtualSwitchPacketsSent | Windows HyperV Server Virtual Switch Packets Sent | Performance | packets/sec | 1.0.0 | HyperV virtual switch packets sent per second. | |
| Windows HyperV Host Disk | windows_hyperv_disk_PhysicalDiskTransferPerSec | Windows HyperV Disk Physical Disk Transfer Per Sec | Performance | IOPS | 1.0.0 | HyperV physical disk transfers per second. |
| windows_hyperv_disk_PhysicalDiskQueueLength | Windows HyperV Disk Physical Disk Queue Length | Performance | 1.0.0 | HyperV physical disk queue length. | ||
| windows_hyperv_disk_PhysicalDiskBytesPerSec | Windows HyperV Disk Physical Disk Bytes Per Sec | Performance | Bps | 1.0.0 | HyperV physical disk bytes per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_disk_PhysicalDiskReadBytesPersec | Windows HyperV Disk Physical Disk Read Bytes Per Sec | Performance | Bps | 1.0.0 | HyperV physical disk read bytes per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_disk_PhysicalDiskReadsPersec | Windows HyperV Disk Physical Disk Reads Per Sec | Performance | Bps | 1.0.0 | HyperV physical disk reads per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_disk_PhysicalDiskWritesPersec | Windows HyperV Disk Physical Disk Writes Per Sec | Performance | Bps | 1.0.0 | HyperV physical disk writes per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_disk_PhysicalDiskWriteBytesPersec | Windows HyperV Disk Physical Disk Write Bytes Per Sec | Performance | Bps | 1.0.0 | HyperV physical disk write bytes per second. | |
| windows_hyperv_disk_HealthStatus | Windows HyperV Disk Health Status | Availability | 1.0.0 | HyperV disk health status. Possible states are: 'Unknown': 0 ,'Failing' : 1, 'Failed' : 2, 'Healthy' : 3 | ||
| windows_hyperv_disk_OperationalStatus | Windows HyperV Disk Operational Status | Availability | 1.0.0 | HyperV disk operational status. Possible statuses are: 'Unknown': 0, 'Not Ready': 1, 'No Media' : 2, 'Offline' : 3, 'Failed': 4, 'Missing' : 5, 'Online': 6 | ||
| Windows HyperV Guest VM | windows_hyperv_guestvm_SnapshotCount | Windows HyperV GuestVM Snapshot Count | Availability | Count | 7.0.0 | Windows HyperV GuestVM Snapshot Count |
| windows_hyperv_guestvm_SnapshotAge | Windows HyperV GuestVM Snapshot Age | Availability | Days | 7.0.0 | Windows HyperV GuestVM Snapshot Age | |
| windows_hyperv_guestvm_CpuUtilization | Windows HyperV GuestVM CPU Utilization | Usage | % | 1.0.0 | HyperV guest VM cpu utilization. | |
| windows_hyperv_guestvm_replicationState | Windows HyperV GuestVM Replication State | Availability | - | 6.0.0 | HyperV Guest VM Replication State.Possible values are ERROR : 0,FAILOVERWAITINGCOMPLETION : 1,FAILEDOVER : 2,NOTAPPLICABLE : 3,READYFORINITIALREPLICATION : 4,REPLICATING : 5,RESYNCHRONIZING : 6,RESYNCHRONIZESUSPENDED : 7,SUSPENDED : 8,SYNCEDREPLICATIONCOMPLETE : 9,WAITINGFORINITIALREPLICATION : 10,WAITINGFORSTARTRESYNCHRONIZE : 11 | |
| windows_hyperv_guestvm_replicationHealth | Windows HyperV GuestVM Replication Health | Availability | - | 6.0.0 | HyperV Guest VM Replication Health.Possible values are : NORMAL : 0,WARNING : 1,CRITICAL : 2 | |
| windows_hyperv_guestvm_State | Windows HyperV GuestVM State | Availability | 1.0.0 | HyperV guest VM state.Possible values are: Off : 0, Other: 1, Stopping: 2, Saved: 3, Paused: 4, Starting: 5, Reset: 6, Saving: 7, Pausing: 8, Resuming: 9, FastSaved: 10, FastSaving: 11, ForceShutdown: 12, ForceReboot: 13, Hibernated: 14, RunningCritical: 15, OffCritical: 16, StoppingCritical : 17, SavedCritical: 18 PausedCritical: 19, StartingCritical: 20, ResetCritical: 21, SavingCritical: 22, PausingCritical: 23, ResumingCritical: 24, FastSavedCritical: 25, FastSavingCritical: 26, Running: 27 | ||
| windows_hyperv_guestvm_diskUsage | Windows HyperV GuestVM Disk Usage | Usage | MB | 1.0.0 | HyperV guest VM disk usage | |
| Windows HyperV Cluster Role | windows_hyperv_role_RunningStatus | Windows HyperV Role Running Status | Availability | 1.0.0 | HyperV cluster role running status.Possible values: Online : 0, Offline : 1, Failed : 2, PartialOnline : 3, Pending : 4, Unknown : 5 | |
| windows_hyperv_role_FailoverStatus | Windows HyperV Role Failover Status | Availability | 1.0.0 | HyperV cluster role failover status. Possible values: Failedover: 0, No Failover: 1 | ||
| Windows HyperV Cluster Shared Volume | windows_hyperv_csv_Utilization | Windows HyperV CSV Utilization | Usage | % | 1.0.0 | HyperV cluster shared volume utilization. |
| windows_hyperv_csv_Usage | Windows HyperV CSV Usage | Usage | GB | 1.0.0 | HyperV cluster shared volume usage. | |
| windows_hyperv_csv_OperationalStatus | Windows HyperV CSV Operational Status | Availability | 1.0.0 | HyperV cluster shared volume operational status. Possible values: Offline : 0, Failed : 1, Inherited : 2, Initializing : 3, Pending : 4, OnlinePending : 5, OfflinePending : 6, Unknown : 7, Online : 8. | ||
| Windows HyperV Cluster Disk | windows_hyperv_clusterdisk_State | Windows HyperV Cluster Disk State | 1.0.0 | HyperV cluster disk state. Possible values: Offline : 0, Failed : 1, Inherited : 2, Initializing : 3, Pending : 4, OnlinePending : 5, OfflinePending : 6, Unknown : 7, Online : 8 |
Default Monitoring Configurations
Windows-hyper v-cluster has default Global Device Management Policies, Global Templates, Global Monitors and Global Metrics in OpsRamp. You can customize these default monitoring configurations as per your business use cases by cloning respective Global Templates and Global Device Management Policies. We recommend doing this activity before installing the application to avoid noise alerts and data.
Default Global Device Management Policies
You can find the Device Management Policy for each Native Type at Setup > Resources > Device Management Policies. Search with suggested name in global scope. Each Device Management Policy follows below naming convention:
{appName nativeType - version - Mode}Ex: windows-hyperv-cluster Windows HyperV Cluster - 1 - Cluster(i.e, appName = windows-hyperv-cluster, nativeType =Windows HyperV Cluster, version = 1, Mode = Cluster)
Default Global Templates
You can find the Global Templates for each Native Type at Setup > Monitoring > Templates. Search with suggested names in global scope. Each template follows below naming convention:
{appName Mode nativeType 'Template' - version}Ex: windows-hyperv-cluster Cluster Windows HyperV Cluster Template - 1 (i.e, appName = windows-hyperv-cluster , nativeType = Windows HyperV Cluster, version = 1, Mode = Cluster)
Default Global Monitors
You can find the Global Monitors for each Native Type at Setup > Monitoring > Monitors. Search with suggested name in global scope. Each Monitors follows below naming convention:
{monitorKey appName nativeType - version}Ex: Windows HyperV Cluster Monitor windows-hyperv-cluster Windows HyperV Cluster 1 (i.e, monitorKey = Windows HyperV Cluster Monitor, appName = windows-hyperv-cluster , nativeType = Windows HyperV Cluster , version= 1)
Configure and Install the Windows HyperV Cluster Integration
- To select your client, navigate to All Clients, and click the Client/Partner dropdown menu.
Note: You may either type your client’s name in the search bar or select your client from the list. - Navigate to Setup > Account. The Account Details screen is displayed.
- Click Integrations. The Installed Integrations screen is displayed with all the installed applications.
Note: If you do not have any installed applications, you will be navigated to the Available Integrations and Apps page with all the available applications along with the newly created application with the version. - Click + ADD on the Installed Integrations page. Note: Search for the integration either by entering the name of the integration in the search bar or by selecting the category of the integration from the All Categories dropdown list.
- Click ADD in the Windows HyperV Cluster application.
- In the Configuration page, click + ADD. The Add Configuration page appears.
- Enter the following BASIC INFORMATION:
| Field Name | Description | Field Type |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Enter the name for the configuration. | String |
| Mode | choose Cluster or Standalone based the providing Windows HyperV configuration.
| Dropdown |
| IP Address/Host Name of Hyper-V cluster | Enter the IP address/host name of the Hyper-V Cluster. It should be accessible from Gateway. | String |
| Is Secure | Select this checkbox if you want the communication between your system and the specified endpoint to be secured using protocols such as HTTPS (HTTP over SSL/TLS). Default Selection:7 When selected, it signifies that the connection is encrypted, providing an added layer of security to the data being transmitted. | Checkbox |
| Windows Cluster Credentials | Select the credential associated with your account. If you want to use the existing credentials, select them from the Select Credentials dropdown. Else, click + Add to create credentials. The ADD CREDENTIAL window is displayed. Enter the following information.
| Dropdown |
| App Failure Notifications | When selected, you will be notified in case of an application failure such as Connectivity Exception, Authentication Exception. | Checkbox |
| Request Timeouts | Select the checkbox to configure the timeout settings for NativeBridge connections and script execution requests made by the integration to the end device. | Checkbox |
| Connection TimeOut In Mins | Select the maximum time, in minutes, that the integration should wait while establishing a connection with the nativeBridge. Default value: 10 minutes | Dropdown |
| Connection Request TimeOut In Mins | Select the maximum time, in minutes, required to process a NativeBridge HTTP call, from sending the request to receiving the response. Default value: 10 minutes | Dropdown |
| Socket Timeout In Mins | Select the maximum allowable time of inactivity between two data packets during data exchange with the server. Default value: 10 minutes | Dropdown |
| Script Execution TimeOut In Mins | Select the maximum time, in minutes, that the integration should wait while establishing a connection with the nativeBridge. Default value: 10 minutes | Dropdown |
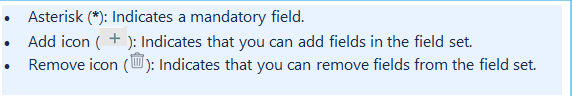
- CUSTOM ATTRIBUTES: Custom attributes are the user-defined data fields or properties that can be added to the preexisting attributes to configure the integration.
| Field Name | Description | Field Type |
|---|---|---|
| Custom Attribute | Select the custom attribute from the dropdown. You can add attributes by clicking the Add icon (+). | Dropdown |
| Value | Select the value from the dropdown. | Dropdown |
Note: The custom attribute that you add here will be assigned to all the resources that are created by the integration. You can add a maximum of five custom attributes (key and value pair).
In the RESOURCE TYPE section, select:
- ALL: All the existing and future resources will be discovered.
- SELECT: You can select one or multiple resources to be discovered.
In the DISCOVERY SCHEDULE section, select recurrence pattern to add one of the following patterns:
- Minutes
- Hourly
- Daily
- Weekly
- Monthly
Click ADD.
Now the configuration is saved and displayed on the configurations page after you save it. From the same page, you may Edit and Remove the created configuration..
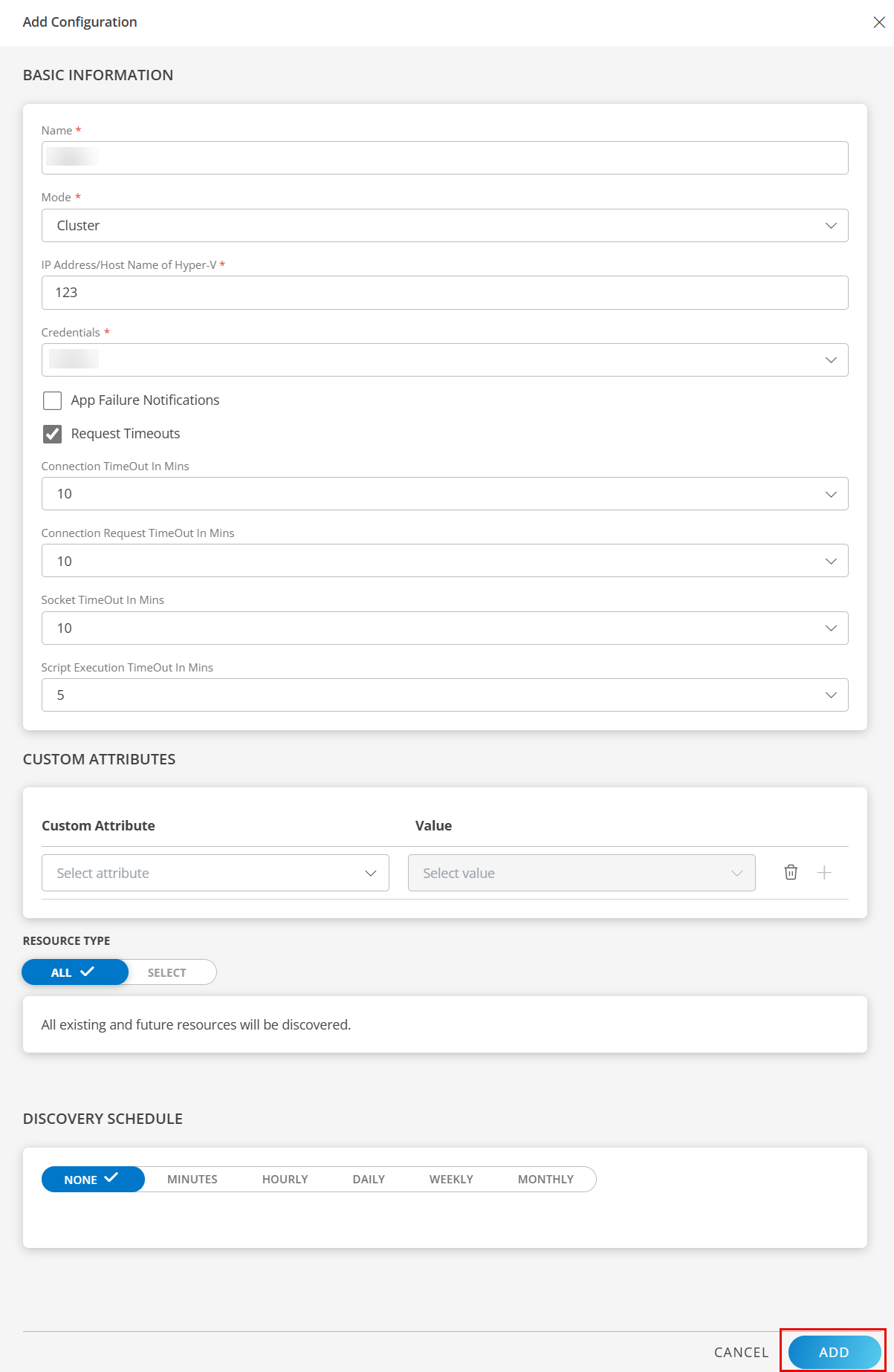
Click NEXT.
In the Installation page, select an existing registered profile, and click FINISH.
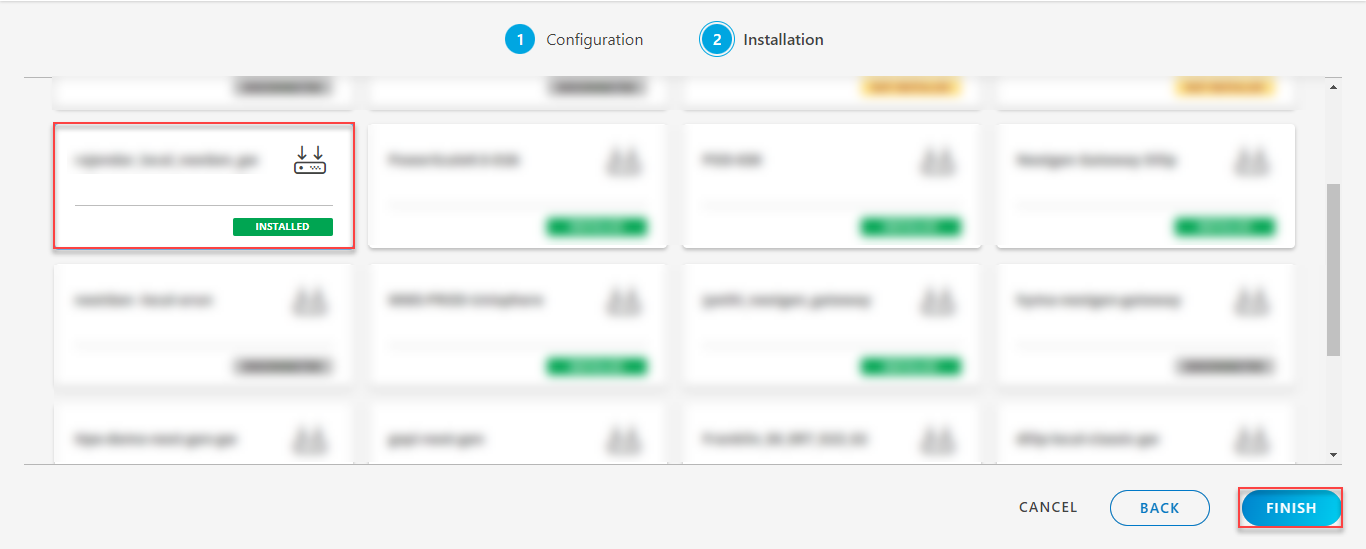
The application is now installed and displayed on the Installed Integration page. Use the search field to find the installed application.
Modify the Configuration
See Modify an Installed Integration or Application article.
Note: Select the Windows HyperV Cluster application.
View the Windows HyperV Cluster Details
- Navigate to Infrastructure > Search > Virtualization > Windows HyperV Cluster. The search result is displayed.
- Click anywhere in the row. A slide-out appears displaying the resource summary. It also has the Overview, Related Resources, and Custom Attributes tabs.
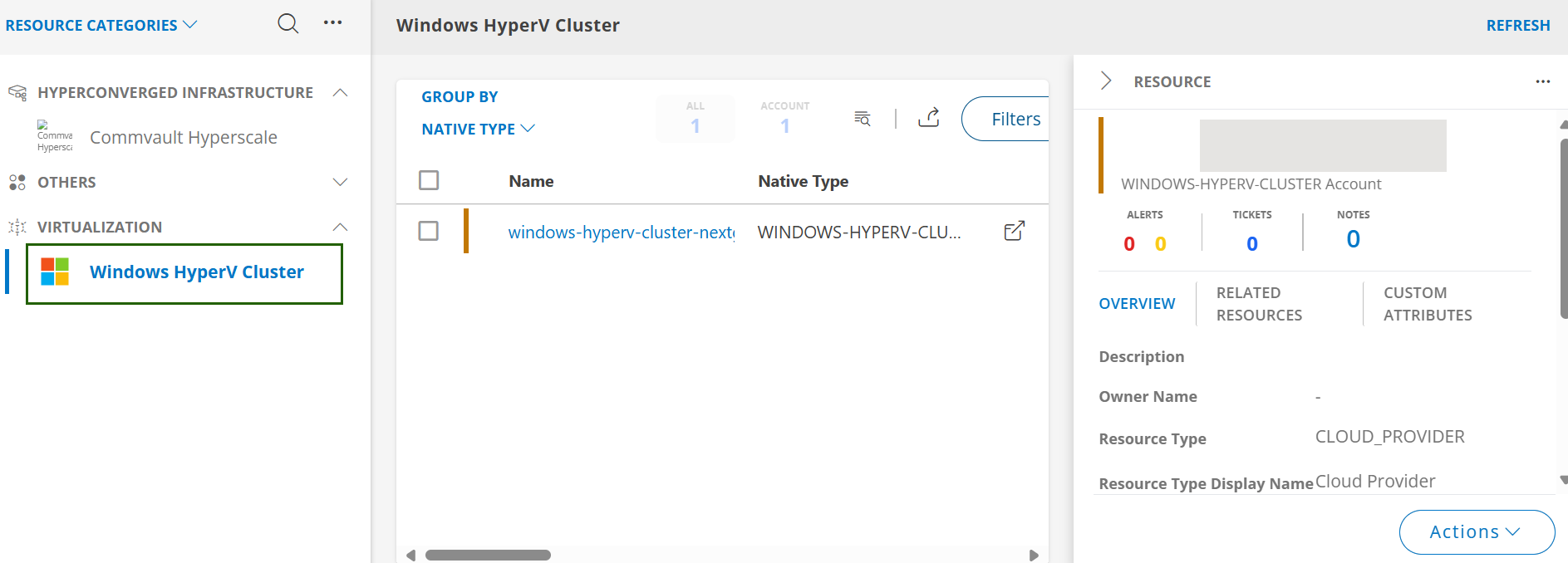
- Click the resource name. The resources details screen is displayed.
- Click the ATTRIBUTES tab to view the discovery details.
View resource metrics
To confirm Windows HyperV Cluster monitoring, review the following:
- Metric graphs: A graph is plotted for each metric that is enabled in the configuration.
- Alerts: Alerts are generated for metrics that are configured as defined for integration.
- Click the METRICS tab to view the metric details for Windows HyperV Cluster.
Resource Filter Input Keys
Click here to view the Resource Filter Input Keys
| Resource Type | Supported Input Key |
|---|---|
| All Types | resourceName |
| hostName | |
| aliasName | |
| dnsName | |
| ipAddress | |
| macAddress | |
| os | |
| make | |
| model | |
| serialNumber | |
| Windows HyperV Cluster | Domain |
| SharedVolumesRoot | |
| Description | |
| Windows HyperV Virtual Switch | description |
| Root Resource UUID | |
| Root Resource IPAddress | |
| Root Resource Name | |
| Root Resource HostName | |
| Root Resource SerialNumber | |
| Windows HyperV Host Disk | NumberOfPartitions |
| ProvisioningType | |
| PartitionStyle | |
| DiskNumber | |
| Root Resource UUID | |
| Root Resource IPAddress | |
| Root Resource Name | |
| Root Resource HostName | |
| Root Resource SerialNumber | |
| Windows HyperV Guest VM | Path |
| CreationTime | |
| ProcessorCount | |
| IsClustered | |
| Root Resource UUID | |
| Root Resource IPAddress | |
| Root Resource Name | |
| Root Resource HostName | |
| Root Resource SerialNumber | |
| Windows HyperV Cluster Role | IsCoreGroup |
| OwnerNode | |
| Root Resource UUID | |
| Root Resource IPAddress | |
| Root Resource Name | |
| Root Resource HostName | |
| Root Resource SerialNumber | |
| Windows HyperV Cluster Disk | OwnerGroup |
| OwnerNode | |
| ResourceType | |
| Root Resource UUID | |
| Root Resource IPAddress | |
| Root Resource Name | |
| Root Resource HostName | |
| Root Resource SerialNumber | |
| Windows HyperV Cluster Shared Volume | OwnerNode |
| FriendlyVolumeName | |
| FileSystem | |
| Root Resource UUID | |
| Root Resource IPAddress | |
| Root Resource Name | |
| Root Resource HostName | |
| Root Resource SerialNumber |
Supported Alert Custom Macros
Customise the alert subject and description with below macros then it will generate alert based on customisation.
Supported macros keys:
- ${resource.name}
- ${resource.ip}
- ${resource.mac}
- ${resource.aliasname}
- ${resource.os}
- ${resource.type}
- ${resource.dnsname}
- ${resource.alternateip}
- ${resource.make}
- ${resource.model}
- ${resource.serialnumber}
- ${resource.systemId}
- ${Custome Attributes in the resource}
- ${parent.resource.name}
Risks, Limitations & Assumptions
- The integration can manage critical/recovery failure alerts for the following two scenarios when the user activates App Failure Notifications in the settings:
- Connectivity Exception
- Authentication Exception
- Application will not send any duplicate/repeat failure alert notification until the already existing critical alert is recovered.
- Using metrics for monitoring the resources and generating alerts when the threshold values are breached.
- Application cannot control monitoring pause/resume actions based on above alerts.
- This application supports both Classic Gateway and NextGen Gateway.
- Not supported with Cluster Gateway.
- The Template Applied Time will only be displayed if the collector profile (Classic and NextGen Gateway) is version 18.1.0 or higher.
- For a Windows HyperV cluster, If Standalone Mode is selected part of configuration, only Windows HyperV Server will get created/updated. Windows HyperV Cluster wont be discovered and will get deleted if already exists.
- Latest snapshot metric support from gateway version 14.0.0.
- Component level thresholds can be configured on each resource level.
Version History
| Application Version | Bug fixes / Enhancements |
|---|---|
| 8.0.0 |
|
| 7.0.1 | Removed resourceName prefix from the attributes make & model for native type Windows HyperV Server. |
| 7.0.0 |
|
| 6.0.0 |
|
| 5.0.0 |
|
| 4.0.0 |
|
| 3.0.1 | Code fix for latest snapshot metric. |
| 3.0.0 | Persona changes to support Cluster and Standalone Windows HyperV Cluster configurations. |
| 2.0.0 |
|
Click here to view the earlier version updates
| Application Version | Bug fixes / Enhancements |
|---|---|
| 1.0.2 | Full discovery support. |
| 1.0.1 | Resource discovery and monitoring implementations. |